Creating Effective Evacuation Notices for Business Safety

Implementing comprehensive evacuation plans is crucial for any business to ensure the safety and well-being of its employees, customers, and visitors. A well-designed evacuation notice is a vital component of this process, providing clear and concise instructions during emergency situations. In this guide, we will explore 15 essential evacuation notice examples, offering valuable insights and tips to help you prepare your business for any eventuality.
1. Evacuation Plan Overview

An evacuation notice should begin with a concise overview of the evacuation plan, outlining the primary objectives and key steps. This section sets the tone for the entire notice, ensuring that readers understand the importance of the information provided.
- Objective: Inform employees and visitors about the evacuation procedure and assembly points.
- Key Steps:
- Step 1: Sound the alarm and initiate the evacuation process.
- Step 2: Proceed to the nearest exit or designated evacuation route.
- Step 3: Gather at the designated assembly point for a headcount.
- Step 4: Await further instructions from emergency personnel.
2. Evacuation Routes and Exits

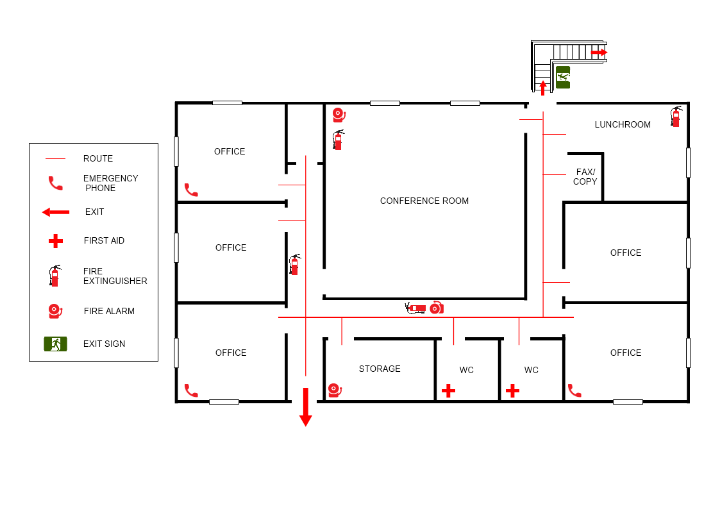
Clearly marking and identifying evacuation routes and exits is essential for a swift and safe evacuation. This section of the notice should provide detailed information on the available routes and exits, ensuring that everyone is aware of their options.
Evacuation Routes:
- Primary Route: Describe the primary evacuation route, including any potential hazards or obstacles.
- Alternative Routes: Outline alternative routes in case the primary route is blocked or unsafe.
Exits:
- Main Exit: Specify the location and accessibility of the main exit.
- Emergency Exits: Highlight the presence of emergency exits and their intended use.
- Special Considerations: Address any special considerations, such as exits for individuals with disabilities.
3. Assembly Points and Headcounts

Designating assembly points and conducting headcounts are crucial steps in ensuring the safety of everyone during an evacuation. This section should provide clear instructions on where to gather and the importance of accurate headcounts.
Assembly Points:
- Primary Assembly Point: Specify the location of the primary assembly point, ideally in an open area away from buildings.
- Alternative Assembly Points: Provide details on alternative assembly points in case the primary point is inaccessible.
Headcounts:
- Procedure: Explain the headcount process, emphasizing the importance of accountability.
- Reporting Absences: Instruct employees on how to report missing individuals to emergency personnel.
4. Emergency Equipment and Supplies

Evacuation notices should also include information on emergency equipment and supplies available within the facility. This ensures that individuals are aware of the resources at their disposal during an emergency.
Fire Extinguishers:
- Location: Indicate the placement of fire extinguishers throughout the building.
- Usage: Provide basic instructions on how to operate a fire extinguisher.
First Aid Kits:
- Availability: Specify the locations of first aid kits and their contents.
- Training: Encourage employees to undergo basic first aid training.
Emergency Lighting:
- Functionality: Explain the purpose of emergency lighting and its activation.
- Maintenance: Highlight the importance of regular maintenance checks.
5. Special Considerations for Different Scenarios

Different emergency scenarios may require specific considerations and actions. This section of the evacuation notice should address common scenarios and provide tailored instructions.
Fire Emergencies:
- Actions: Outline the steps to take in case of a fire, including sounding the alarm and evacuating.
- Smoke Inhalation: Provide guidance on how to protect oneself from smoke inhalation.
Natural Disasters:
- Earthquakes: Instruct employees on the “drop, cover, and hold” technique.
- Floods: Specify safe evacuation routes and potential hazards.
Medical Emergencies:
- CPR and AED: Emphasize the importance of CPR training and AED locations.
- Evacuation of Injured Individuals: Offer guidelines for assisting injured colleagues during an evacuation.
6. Communication and Reporting Procedures

Effective communication is vital during an evacuation. This section should detail the communication channels and reporting procedures to be followed during an emergency.
Internal Communication:
- Intercom System: Describe the use of the intercom system for broadcasting emergency updates.
- Emergency Phones: Provide information on the location and purpose of emergency phones.
External Communication:
- Emergency Contacts: List emergency contact numbers for local authorities and emergency services.
- Media Updates: Explain the process for providing updates to the media during a crisis.
Reporting Incidents:
- Procedure: Outline the steps for reporting an emergency to the relevant authorities.
- Incident Reports: Instruct employees on completing incident reports after an evacuation.
7. Training and Practice Drills
Regular training and practice drills are essential to ensure that employees are familiar with the evacuation procedures. This section should emphasize the importance of ongoing training and provide details on the training schedule.
Training Sessions:
- Frequency: Specify the frequency of training sessions, such as quarterly or biannually.
- Topics Covered: List the key topics covered in the training, including fire safety and first aid.
Practice Drills:
- Schedule: Announce the dates and times of upcoming practice drills.
- Realistic Scenarios: Encourage employees to treat drills as real-life situations.
Feedback and Improvements:
- Evaluation: Highlight the importance of evaluating drills for continuous improvement.
- Suggestions: Encourage employees to provide feedback on the evacuation process.
8. Accessibility and Accommodations

Evacuation notices should address the needs of individuals with disabilities or special accommodations. This section should provide guidance on assisting these individuals during an evacuation.
Wheelchair Users:
- Evacuation Procedures: Describe the process for evacuating individuals using wheelchairs.
- Assistance: Emphasize the importance of offering assistance and following their instructions.
Visually Impaired Individuals:
- Guide Dogs: Explain the role of guide dogs during an evacuation and their priority access.
- Evacuation Guidance: Provide instructions on how to guide visually impaired individuals safely.
Hearing Impaired Individuals:
- Visual Alerts: Highlight the use of visual alerts, such as flashing lights, for hearing-impaired individuals.
- Communication Methods: Suggest alternative communication methods, such as written instructions.
9. Emergency Response Team Roles and Responsibilities

Designating an emergency response team and outlining their roles and responsibilities is crucial for a well-coordinated evacuation. This section should provide a clear understanding of the team’s duties.
Team Composition:
- Leader: Identify the leader of the emergency response team and their contact information.
- Members: List the roles and responsibilities of each team member, such as floor monitors or first aid coordinators.
Duties and Responsibilities:
- Leader’s Role: Describe the leader’s responsibilities, including overall coordination and communication.
- Team Member Roles: Outline the specific duties of each team member, such as conducting headcounts or assisting with injured individuals.
10. Post-Evacuation Procedures

Evacuation notices should also cover the post-evacuation procedures to ensure a smooth return to normal operations. This section should provide guidance on what to expect and how to proceed after an evacuation.
Re-entry to the Building:
- Safety Checks: Explain the process of conducting safety checks before re-entry.
- Building Access: Specify who is authorized to grant access to the building post-evacuation.
Damage Assessment:
- Procedure: Outline the steps for assessing any damage to the facility and its contents.
- Reporting Damage: Instruct employees on how to report damage to the appropriate departments.
Business Continuity:
- Backup Plans: Provide information on backup plans and alternative work arrangements if the facility is deemed unsafe.
- Communication with Clients: Offer guidance on communicating with clients and stakeholders during and after an evacuation.
11. Evacuation Notices in Different Languages
For businesses with a diverse workforce or international operations, providing evacuation notices in multiple languages is essential. This section should address the importance of multilingual notices and offer suggestions for implementation.
Language Barriers:
- Impact on Evacuation: Highlight the potential challenges language barriers can pose during an evacuation.
- Translation Services: Encourage the use of translation services to ensure all employees understand the evacuation procedures.
Multilingual Notices:
- Distribution: Suggest distributing evacuation notices in different languages to relevant departments or teams.
- Training in Multiple Languages: Emphasize the need for training sessions conducted in various languages.
12. Visual Aids and Signage
Visual aids and signage play a crucial role in guiding individuals during an evacuation. This section should emphasize the importance of clear and visible signage throughout the facility.
Evacuation Maps:
- Placement: Specify the locations where evacuation maps should be displayed, such as near exits or in common areas.
- Content: Ensure that evacuation maps are up-to-date and include all relevant information, including assembly points and emergency equipment.
Signage:
- Exit Signs: Highlight the importance of well-lit and visible exit signs, especially in low-light conditions.
- Assembly Point Signs: Encourage the use of signs indicating assembly points to guide individuals during an evacuation.
Floor Plans:
- Distribution: Provide floor plans to emergency response teams and relevant departments for better understanding of the facility layout.
- Updates: Emphasize the need for regular updates to floor plans to reflect any changes in the building’s layout.
13. Emergency Supplies and Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance and inspection of emergency supplies and equipment are essential to ensure their functionality during an emergency. This section should outline the maintenance procedures.
Fire Extinguishers:
- Inspection: Specify the frequency of fire extinguisher inspections, typically annually or semi-annually.
- Recharging: Explain the process of recharging fire extinguishers and the importance of using certified technicians.
First Aid Kits:
- Inventory Checks: Instruct designated individuals to conduct regular inventory checks of first aid kits.
- Replenishment: Provide guidance on replenishing first aid kits with expired or depleted supplies.
Emergency Lighting:
- Battery Checks: Highlight the need for regular battery checks in emergency lighting systems.
- Replacement: Offer instructions on replacing faulty or expired batteries to ensure continuous functionality.
14. Emergency Contact Information
Providing emergency contact information is vital for quick and efficient communication during an emergency. This section should list the contact details of key personnel and emergency services.
Emergency Contacts:
- Facility Manager: Provide the contact information of the facility manager or a designated emergency contact.
- Local Authorities: List the contact details of local police, fire, and emergency medical services.
Emergency Hotline:
- Establish a Hotline: Consider setting up an emergency hotline specifically for reporting emergencies and seeking assistance.
- Promote Awareness: Ensure that the hotline number is prominently displayed throughout the facility.
15. Regular Updates and Revisions
Evacuation notices should be regularly updated and revised to reflect any changes in the facility, emergency procedures, or relevant regulations. This section should emphasize the importance of keeping the notices current.
Review and Update Frequency:
- Annual Review: Suggest conducting an annual review of the evacuation notices to ensure their accuracy and relevance.
- Changes in Facility: Highlight the need to update notices whenever there are significant changes to the facility’s layout or emergency equipment.
Feedback and Improvements:
- Employee Feedback: Encourage employees to provide feedback on the evacuation notices and suggest improvements.
- External Audits: Consider conducting regular external audits to identify areas for enhancement in the evacuation plan.
Conclusion

Creating comprehensive and effective evacuation notices is a critical aspect of business safety and emergency preparedness. By following the examples and guidelines outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your business is well-equipped to handle any emergency situation. Remember, a well-prepared evacuation plan can make a significant difference in protecting lives and minimizing potential losses. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and keep your evacuation notices up-to-date to maintain a safe and secure work environment.
FAQ

How often should evacuation notices be updated and revised?
+Evacuation notices should be updated at least once a year to account for any changes in the facility, emergency procedures, or relevant regulations. However, it is recommended to review and update notices whenever there are significant changes to the building layout, emergency equipment, or personnel.
What should be included in an evacuation notice for a business with multiple floors or buildings?
+For businesses with multiple floors or buildings, the evacuation notice should provide specific instructions for each area. This includes detailing the evacuation routes, assembly points, and any special considerations, such as using elevators during an evacuation.
How can I ensure that employees with limited English proficiency understand the evacuation procedures?
+To accommodate employees with limited English proficiency, provide evacuation notices in multiple languages. Additionally, consider conducting training sessions in their native language and encourage them to ask questions or seek clarification from bilingual colleagues or supervisors.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating evacuation notices?
+Common mistakes to avoid include using complex language or jargon that may be difficult to understand, omitting important details such as assembly points or emergency contacts, and failing to regularly update and maintain the notices. It is also crucial to ensure that evacuation notices are visible and easily accessible to all employees and visitors.
How can I encourage employees to actively participate in evacuation drills and training sessions?
+To encourage employee participation in evacuation drills and training sessions, make them engaging and interactive. Provide incentives or rewards for active participation, recognize and acknowledge employees who demonstrate exceptional preparedness, and regularly communicate the importance of these drills for their safety and well-being.