Introduction to Crop Rotation

Crop rotation is an agricultural practice that involves the strategic sequencing of different crops in the same field over multiple growing seasons. By rotating crops, farmers can enhance soil health, manage pests and diseases, and optimize nutrient availability. This ancient technique has been employed for centuries and is still widely practiced today, offering numerous benefits to both conventional and organic farming systems. In this blog post, we will explore five effective ways to create a perfect crop rotation plan, ensuring sustainable and productive agricultural practices.
1. Understanding Crop Families and Compatibility

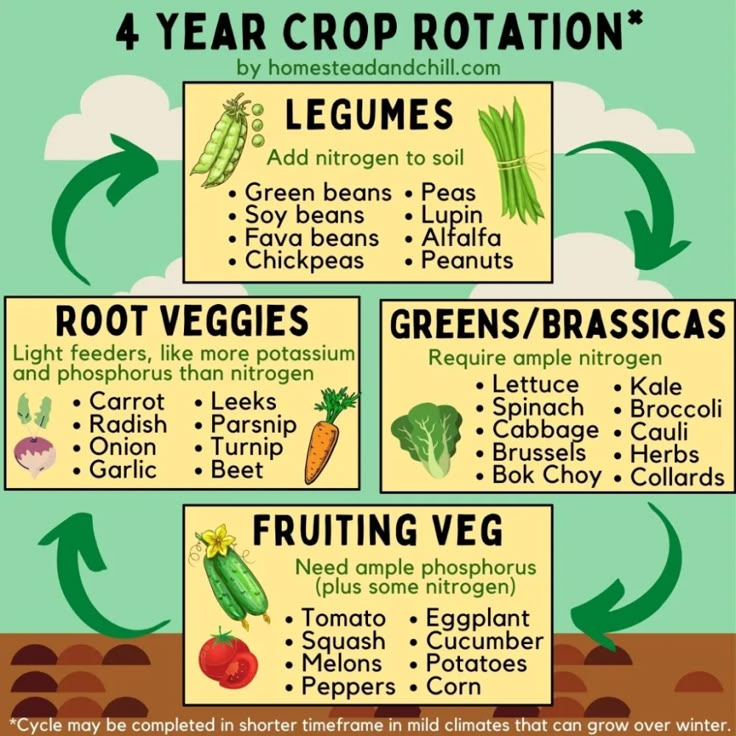
The first step in creating an effective crop rotation plan is to gain a thorough understanding of crop families and their compatibility. Crops can be categorized into different families based on their botanical relationships and nutritional requirements. Familiarize yourself with the common crop families, such as the Brassica family (cabbage, broccoli), the Solanaceae family (tomatoes, potatoes), and the Fabaceae family (beans, peas).
Understanding Compatibility: - Nutrient Needs: Different crop families have varying nutrient requirements. Some crops are heavy feeders, depleting specific nutrients from the soil, while others are more balanced or even improve soil fertility. - Pest and Disease Control: Crop rotation can help manage pests and diseases by disrupting their life cycles. Avoid planting crops from the same family in consecutive years, as pests and diseases often target specific families. - Soil Health: Certain crops are known for their ability to improve soil structure and fertility. Legumes, for example, fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting subsequent crops that require higher nitrogen levels.
2. Identifying Your Farm’s Unique Needs and Goals

Every farm is unique, with its own set of challenges and opportunities. It’s crucial to tailor your crop rotation plan to your specific farm’s needs and goals. Consider the following factors:
- Soil Type and Quality: Assess your soil’s texture, pH level, and nutrient content. Different crops thrive in specific soil conditions, so choose crops that are well-suited to your soil type.
- Climate and Growing Season: Evaluate your farm’s climate and the length of your growing season. Some crops are more adaptable to different climates, while others have specific temperature and sunlight requirements.
- Market Demand and Crop Value: Research the market demand for various crops in your region. Consider the potential profitability and consumer preferences when selecting crops for your rotation plan.
- Labor and Equipment Availability: Evaluate your farm’s labor capacity and the availability of specialized equipment. Some crops may require more intensive labor or specific machinery, so plan accordingly.
3. Choosing the Right Crops for Your Rotation

Selecting the right crops for your rotation plan is crucial for its success. Consider the following criteria when choosing crops:
- Diversity: Aim for a diverse crop rotation to maximize the benefits. Include crops from different families to enhance soil health and reduce the risk of pest and disease buildup.
- Succession Planting: Plan for succession planting, where you sow or transplant crops at different times to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season.
- Cover Crops: Incorporate cover crops into your rotation plan. Cover crops, such as clover or rye, can help suppress weeds, improve soil structure, and prevent erosion during fallow periods.
- Crop Compatibility: Pay attention to crop compatibility. Some crops, when grown together, can have synergistic effects, improving each other’s growth and health.
- Crop Rotation Groups: Organize your chosen crops into rotation groups based on their families and compatibility. This will help you plan a balanced and effective rotation sequence.
4. Designing a Balanced Crop Rotation Plan

A well-designed crop rotation plan should aim for balance and diversity. Consider the following principles when creating your plan:
- Three-Year or Four-Year Rotation: A common practice is to design a three- or four-year crop rotation plan. This allows for a good mix of crops and provides enough time for soil recovery and pest and disease management.
- Alternating Crop Families: Ensure that you alternate crop families in your rotation. For example, follow a Brassica crop with a legume crop, and then a cereal crop, to maximize soil health benefits.
- Consideration of Nutrient Management: Pay attention to the nutrient needs of each crop. Plan your rotation to ensure that crops with high nutrient demands are followed by those that replenish the soil, such as legumes fixing nitrogen.
- Rotation with Perennial Crops: If you have perennial crops, such as fruit trees or vines, consider how they fit into your rotation plan. Perennial crops can provide long-term benefits but may also require specific management strategies.
5. Implementing and Monitoring Your Crop Rotation Plan

Once you have designed your crop rotation plan, it’s time to put it into action and monitor its effectiveness. Here are some key steps to ensure successful implementation:
- Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed records of your crop rotation plan, including the types of crops, planting dates, and harvest dates. This will help you evaluate the plan’s success and make informed adjustments in the future.
- Soil Testing: Regularly test your soil to monitor nutrient levels and pH. This information will guide your fertilization and amendment strategies, ensuring optimal soil health.
- Pest and Disease Management: Stay vigilant for signs of pest and disease outbreaks. Crop rotation is an effective pest management strategy, but it’s essential to monitor and take action if necessary.
- Crop Rotation Adjustment: Be prepared to adjust your crop rotation plan based on your observations and soil test results. Flexibility is key to optimizing your plan over time.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest research and best practices in crop rotation. Attend workshops, read agricultural publications, and connect with other farmers to exchange knowledge and experiences.
Conclusion

Creating a perfect crop rotation plan is a strategic and thoughtful process that requires a deep understanding of crop families, farm-specific needs, and the principles of sustainable agriculture. By following the five ways outlined in this blog post, you can develop a well-designed and effective crop rotation plan that enhances soil health, manages pests and diseases, and optimizes crop production. Remember, crop rotation is a long-term strategy, and its benefits will become more evident over time as your soil health improves and your farm becomes more resilient.
🌱 Note: Crop rotation is a dynamic process, and it's important to adapt your plan based on your farm's unique conditions and observations. Stay flexible and open to adjustments to ensure the best outcomes for your agricultural practices.
FAQ

What are the benefits of crop rotation for soil health?
+
Crop rotation improves soil health by enhancing soil structure, increasing organic matter, and promoting beneficial microbial activity. It also helps prevent nutrient depletion and reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases.
How often should I rotate my crops?

+
A typical crop rotation plan spans three to four years. However, the frequency of rotation depends on your specific farm’s needs, crop choices, and goals. Some farms may benefit from shorter or longer rotations.
Can I rotate crops within a single growing season?

+
Yes, you can practice intra-seasonal crop rotation by intercropping or planting multiple crops in the same field at different times. This can help maximize space utilization and provide additional benefits to your farm ecosystem.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in crop rotation planning?

+
Common mistakes include neglecting soil testing, failing to consider crop compatibility, and not adapting the plan to changing farm conditions. It’s crucial to stay informed and flexible to ensure the success of your crop rotation.
How can I find more resources and support for crop rotation planning?

+
You can seek guidance from local agricultural extension offices, attend farming workshops and conferences, and connect with experienced farmers in your region. Online resources and agricultural publications can also provide valuable insights.