Achieving realistic and visually appealing ambient occlusion in your 3D scenes is an art, and with the right techniques, you can elevate your rendering quality to new heights. Ambient occlusion, often abbreviated as AO, is a shading technique used to add depth and realism to 3D models by simulating how light interacts with surfaces and objects. In this blog post, we will explore six essential tips to help you master ambient occlusion and take your 3D artwork to the next level.
1. Understand Ambient Occlusion

Before diving into the technical aspects, it's crucial to grasp the concept of ambient occlusion. Ambient occlusion is a lighting technique that calculates how much ambient light reaches different parts of a 3D model. It considers the surrounding geometry and determines the level of illumination based on the presence of other objects or surfaces nearby. By understanding this, you can make informed decisions when setting up your AO parameters.
2. Choose the Right AO Method

There are several methods to generate ambient occlusion, each with its own advantages and use cases. Some popular methods include:
- Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO): A real-time AO technique that calculates occlusion based on depth information from the camera's perspective. It's ideal for real-time applications like games.
- Horizon-Based Ambient Occlusion (HBAO): Similar to SSAO, HBAO considers the horizon and the angle of incidence to determine occlusion. It often produces more accurate results but requires more computational power.
- Ray-Traced Ambient Occlusion: This method traces rays from each point on the surface to simulate how light would interact with the environment. While computationally intensive, it offers the highest quality results.
Consider the specific needs of your project and the hardware limitations when choosing an AO method.
3. Adjust AO Parameters

Once you've selected an AO method, fine-tuning the parameters is essential to achieve the desired result. Here are some key parameters to experiment with:
- Radius: Controls the distance over which ambient occlusion is calculated. A larger radius can capture more detail but may introduce noise.
- Intensity: Determines the strength of the ambient occlusion effect. Adjusting this value can make your scenes appear more or less shaded.
- Bias: Allows you to control how much ambient light is blocked by nearby geometry. A higher bias can create a more dramatic effect.
- Samples: Increasing the number of samples can improve the quality of the AO, but it also increases rendering time.
Play around with these parameters to find the perfect balance for your scene.
4. Combine AO with Other Lighting Techniques

Ambient occlusion works best when combined with other lighting techniques. Consider using it alongside global illumination, image-based lighting, or even simple directional lights to create a more realistic and visually appealing scene. By combining multiple lighting methods, you can achieve a well-balanced and natural-looking environment.
5. Optimize Performance

Depending on the complexity of your scene and the chosen AO method, ambient occlusion can be computationally demanding. To optimize performance, consider the following:
- Use a lower resolution for AO calculations if real-time performance is crucial.
- Implement AO as a post-process effect to reduce the impact on rendering times.
- Experiment with different AO methods to find the one that strikes the right balance between quality and performance.
6. Bake Ambient Occlusion
For static scenes or when real-time performance is not a concern, baking ambient occlusion can be a powerful technique. Baking involves pre-computing the AO values and storing them as a texture or a set of vertices. This approach saves rendering time and can be particularly useful for architectural visualizations or game assets.
To bake ambient occlusion, you'll need to set up a light probe or an indirect lighting solution in your 3D software. The software will then calculate and store the AO values for each point on the surface, which can be applied as a texture or vertex color during rendering.
Examples of Ambient Occlusion in Action

To help visualize the impact of ambient occlusion, let's take a look at some before-and-after examples. The following images showcase how ambient occlusion can add depth and realism to 3D scenes:

In the above image, ambient occlusion was applied to the room, adding subtle shadows and enhancing the sense of depth. The scene feels more immersive and realistic with AO.

Here, ambient occlusion was used to bring out the details of the character's clothing and the surrounding environment. Notice how the creases and folds become more pronounced, creating a more lifelike appearance.
Additional Tips and Tricks

- Experiment with different AO methods and parameters to find the perfect balance for your project.
- Consider using ambient occlusion as a base for further post-processing effects, such as adding film grain or color grading.
- When baking AO, ensure that your light probe or indirect lighting setup accurately represents the scene's lighting conditions.
🌟 Note: Remember that ambient occlusion is just one tool in your 3D rendering arsenal. Combine it with other techniques to create stunning and photorealistic scenes.
Conclusion
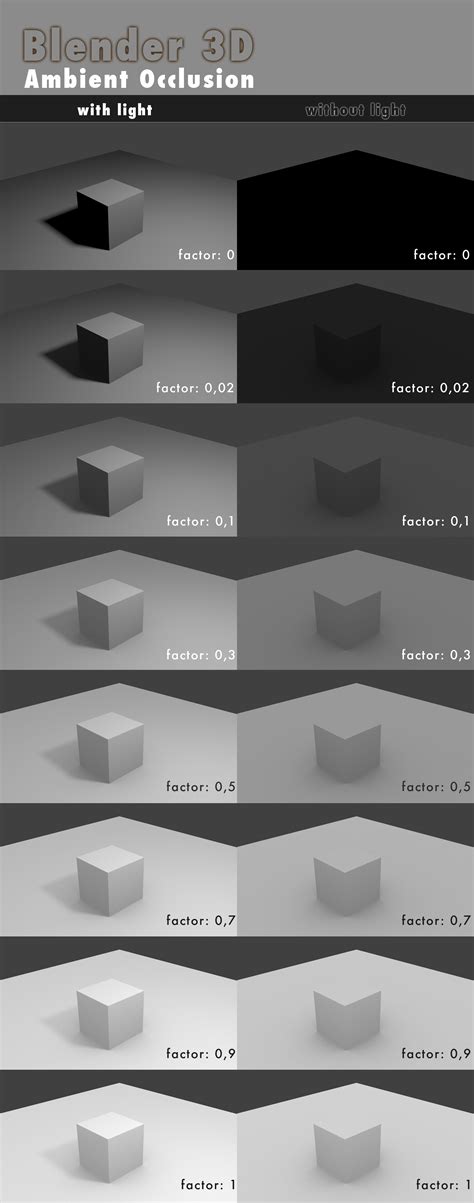
Mastering ambient occlusion is an essential skill for any 3D artist or developer. By understanding the concept, choosing the right AO method, and fine-tuning parameters, you can create visually stunning and realistic scenes. Whether you're working on a game, an animation, or a 3D visualization, ambient occlusion will add depth and immerse your audience in your virtual world. With these tips, you're well on your way to achieving stunning results!
What is the main purpose of ambient occlusion in 3D rendering?

+
Ambient occlusion adds depth and realism to 3D scenes by simulating how ambient light interacts with surfaces and objects.
Can I use ambient occlusion in real-time applications like games?

+
Yes, methods like Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO) are designed for real-time applications, offering a balance between quality and performance.
How can I optimize ambient occlusion for better performance?
+
Consider using lower resolution for AO calculations, implementing it as a post-process effect, or experimenting with different AO methods to find the best balance.