What is the Forward Capacity Market?
The Forward Capacity Market (FCM) is a vital component of the energy industry, particularly in the context of electricity generation and transmission. It is a mechanism designed to ensure the long-term reliability and stability of electricity supply by incentivizing the development of new generation capacity and managing the efficient use of existing infrastructure. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Forward Capacity Market, exploring its purpose, functioning, and significance in the energy sector.
Understanding the Basics

The FCM operates as a market-based approach to capacity planning and procurement, aiming to create a balanced and sustainable electricity system. It is a forward-looking market, as the name suggests, where capacity is traded and allocated for future periods, typically several years ahead. This market mechanism plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges of meeting increasing electricity demand while maintaining a reliable and secure grid.
How Does the Forward Capacity Market Work?

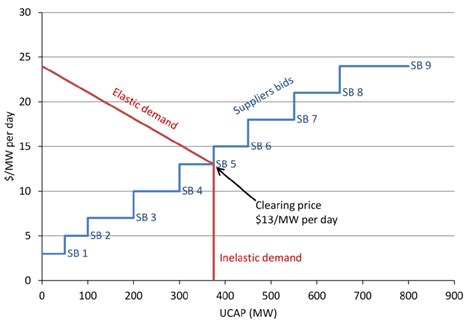
The FCM operates through a series of auctions or capacity auctions, where electricity generators and transmission providers offer their capacity to meet future demand. These auctions are typically organized by regional transmission organizations (RTOs) or independent system operators (ISOs), which are responsible for managing the electricity grid and ensuring its reliability. The process involves the following key steps:
- Capacity Determination: The RTO/ISO assesses the future electricity demand and determines the required capacity to meet this demand. This includes forecasting load growth, considering retirement of existing generation assets, and evaluating the need for new capacity.
- Auction Design: The RTO/ISO designs the capacity auction, defining the rules, eligibility criteria, and clearing prices. This involves setting minimum capacity requirements, establishing bidding parameters, and determining the market structure, such as whether it will be a single- or multi-year auction.
- Participation and Bidding: Eligible market participants, including generators, transmission providers, and sometimes demand-side resources, submit bids for their capacity offerings. Bids are typically based on the cost of providing capacity and the value of the capacity to the market.
- Clearing the Market: The RTO/ISO clears the market by selecting the most cost-effective bids that meet the determined capacity requirements. The clearing price is set at the highest bid price among the selected bids, and all successful bidders receive this price for their capacity.
- Capacity Payments: Successful bidders receive capacity payments, which are essentially payments for providing the committed capacity. These payments provide an incentive for generators to invest in new capacity or maintain existing infrastructure.
- Performance Obligations: Generators and transmission providers are required to meet their committed capacity obligations. Failure to do so may result in penalties or other enforcement measures.
Benefits and Significance
The Forward Capacity Market offers several benefits and plays a significant role in the energy sector:
- Reliability and Security: By incentivizing the development of new generation capacity and ensuring the efficient use of existing infrastructure, the FCM enhances the reliability and security of the electricity grid. It helps prevent blackouts and ensures a stable supply of electricity to meet demand.
- Market Efficiency: The FCM promotes market efficiency by creating a competitive environment for capacity procurement. It encourages generators to offer their capacity at competitive prices, leading to cost-effective solutions for meeting electricity demand.
- Long-Term Planning: The forward-looking nature of the FCM allows for long-term capacity planning. It provides generators and transmission providers with the necessary incentives and certainty to invest in new projects and maintain existing assets, ensuring a sustainable electricity system.
- Risk Management: The FCM helps manage the risks associated with capacity shortages and the retirement of aging generation assets. By providing capacity payments, it encourages the development of new, cleaner, and more efficient generation technologies.
- Integration of Renewables: The FCM can facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. By offering capacity payments for renewable projects, it can encourage the development of wind, solar, and other renewable technologies, contributing to a greener and more sustainable energy mix.
Key Participants and Stakeholders

The Forward Capacity Market involves a range of participants and stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in its functioning:
- Generators: Electricity generators, including traditional fossil fuel plants, nuclear power plants, and renewable energy projects, participate in the FCM by offering their capacity to meet future demand.
- Transmission Providers: Transmission providers, responsible for the infrastructure that transmits electricity from generators to consumers, also participate in the FCM. They ensure the efficient use of transmission capacity and may offer their services in capacity auctions.
- Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organizations (RTOs): ISOs and RTOs are key players in the FCM. They organize and oversee the capacity auctions, determine capacity requirements, and ensure the market’s integrity and fairness.
- Regulators and Policy Makers: Regulatory bodies and policy makers play a vital role in establishing the rules and guidelines for the FCM. They set the framework and provide oversight to ensure the market’s effectiveness and alignment with energy policies.
- Consumers: While consumers do not directly participate in the FCM, they benefit from a reliable and secure electricity supply. The FCM helps maintain stable electricity prices and ensures the availability of electricity to meet their needs.
Market Structure and Variations

The structure and design of the Forward Capacity Market can vary across different regions and jurisdictions. Some common variations include:
- Single-Year vs. Multi-Year Auctions: Some FCMs conduct single-year auctions, where capacity is allocated for a specific year, while others use multi-year auctions, which allocate capacity for multiple years at once. Multi-year auctions provide longer-term certainty for market participants.
- Price-Based vs. Quantity-Based Auctions: FCMs can use price-based auctions, where the clearing price is determined by the highest bid price, or quantity-based auctions, where the clearing price is set based on the quantity of capacity offered.
- Capacity Payment Formulas: The calculation of capacity payments can vary. Some FCMs use a fixed capacity payment formula, while others employ a more dynamic approach, considering factors such as the cost of capacity and the value of the capacity to the market.
- Demand-Side Participation: In some FCMs, demand-side resources, such as energy efficiency measures or demand response programs, are eligible to participate. These resources can offer capacity by reducing electricity demand during peak periods.
Challenges and Considerations

While the Forward Capacity Market offers numerous benefits, it also faces certain challenges and considerations:
- Market Power and Concentration: The FCM can create opportunities for market power and concentration, particularly if a small number of generators dominate the market. Regulatory measures and market monitoring are essential to ensure fair competition and prevent market abuse.
- Technology Transition: The transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources poses challenges for the FCM. As traditional fossil fuel plants retire and renewable energy projects come online, the FCM must adapt to encourage the development of new technologies while ensuring a reliable supply.
- Market Design and Efficiency: The design of the FCM, including auction rules and capacity payment formulas, must be carefully considered to ensure market efficiency and avoid market distortions. Regular reviews and adjustments are necessary to keep pace with changing market conditions.
- Regulatory and Policy Alignment: The FCM operates within the framework of energy policies and regulations. Aligning the market design with broader energy goals and ensuring consistency with other market mechanisms is crucial for its effectiveness.
Case Studies and Examples

To better understand the Forward Capacity Market, let’s explore a few real-world examples:
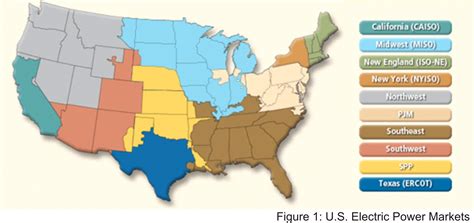
- PJM Interconnection: PJM Interconnection is a regional transmission organization covering a large portion of the eastern United States. It operates one of the largest FCMs, known as the Reliability Pricing Model (RPM). The RPM aims to ensure adequate capacity reserves and maintain a reliable electricity supply in the region.
- New England ISO (ISO-NE): ISO-NE is responsible for managing the electricity grid in the New England region. Its Forward Capacity Market (FCM) is designed to procure sufficient capacity to meet the region’s electricity demand. The FCM in New England has successfully attracted new generation projects, including renewable energy sources.
- Ontario Forward Capacity Market: The Ontario Forward Capacity Market is a capacity auction program implemented by the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) in Ontario, Canada. It aims to ensure adequate electricity supply and encourage the development of new generation capacity. The market has seen participation from a range of generators, including renewable energy projects.
The Future of the Forward Capacity Market

The Forward Capacity Market is expected to continue evolving to meet the changing dynamics of the energy sector. As the world transitions towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future, the FCM will play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources and ensuring a reliable electricity supply. Here are some key trends and developments to watch:
- Integration of Renewables: The FCM will increasingly focus on integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the grid. Capacity payments for renewable projects will become more common, encouraging the development of sustainable generation capacity.
- Flexibility and Demand-Side Participation: The FCM is likely to incorporate more flexibility measures and encourage demand-side participation. This includes incentivizing energy efficiency measures, demand response programs, and the use of energy storage technologies to balance supply and demand.
- Market Design Innovations: FCM designers will continue to explore innovative market structures and mechanisms to enhance market efficiency and fairness. This may include the introduction of new auction formats, capacity payment formulas, and market-based approaches to address specific challenges.
- Data Analytics and Digitalization: The increasing availability of data and advancements in digital technologies will enable more sophisticated analysis and modeling in the FCM. This can lead to improved capacity forecasting, market design, and risk management.
- International Collaboration: As energy markets become more interconnected, international collaboration and harmonization of FCM practices may become more prevalent. This can help address cross-border capacity issues and promote a more integrated and efficient electricity system.
Conclusion
The Forward Capacity Market is a critical mechanism for ensuring the reliability and stability of the electricity grid. By incentivizing the development of new generation capacity and managing the efficient use of existing infrastructure, the FCM plays a vital role in meeting increasing electricity demand. As the energy sector undergoes a transition towards cleaner and more sustainable sources, the FCM will continue to evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities. With its market-based approach, the FCM promotes efficiency, encourages investment in new technologies, and helps integrate renewable energy into the grid. As we move towards a greener and more sustainable energy future, the Forward Capacity Market will remain a key tool in shaping the electricity landscape.
FAQ

What is the primary purpose of the Forward Capacity Market?

+
The primary purpose of the Forward Capacity Market is to ensure the long-term reliability and stability of electricity supply by incentivizing the development of new generation capacity and managing the efficient use of existing infrastructure.
How does the FCM differ from traditional electricity markets?

+
The FCM differs from traditional electricity markets in that it focuses on capacity rather than energy. While traditional markets trade energy based on current demand, the FCM allocates capacity for future periods, ensuring a reliable supply to meet future demand.
What are the key benefits of the Forward Capacity Market?
+The key benefits of the FCM include enhanced reliability and security of the electricity grid, market efficiency through competitive capacity procurement, long-term capacity planning, risk management, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
How does the FCM encourage the development of renewable energy sources?
+The FCM encourages the development of renewable energy sources by offering capacity payments for renewable projects. These payments provide an incentive for the development of wind, solar, and other renewable technologies, contributing to a greener energy mix.
What are some challenges faced by the Forward Capacity Market?
+Challenges faced by the FCM include market power and concentration, the transition to cleaner energy sources, market design and efficiency considerations, and the need for regulatory and policy alignment.
💡 Note: The Forward Capacity Market is a dynamic and evolving mechanism, and its design and structure may vary across different regions and jurisdictions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, but it is essential to consult specific market rules and regulations for detailed information.