In the vast expanse of a desert, where aridity and harsh conditions prevail, one might wonder about the existence of fertile areas. While deserts are often associated with extreme dryness and limited vegetation, there are indeed pockets of fertility that can thrive in these seemingly inhospitable environments. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of fertile areas in deserts, uncovering the secrets behind their existence and the unique adaptations that allow life to flourish in such challenging conditions.
Understanding Desert Ecosystems

Before delving into the fertile areas, it is essential to grasp the characteristics of desert ecosystems. Deserts are defined by their low precipitation levels, intense sunlight, and extreme temperature fluctuations. These harsh environmental factors pose significant challenges to plant and animal life, leading to a unique and specialized ecosystem.
Despite the challenges, deserts are not devoid of life. They are home to a diverse range of species that have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive and even thrive in these conditions. From drought-resistant plants to heat-tolerant animals, desert organisms have developed strategies to conserve water, withstand extreme temperatures, and make the most of limited resources.
Oases: The Desert's Lifeline
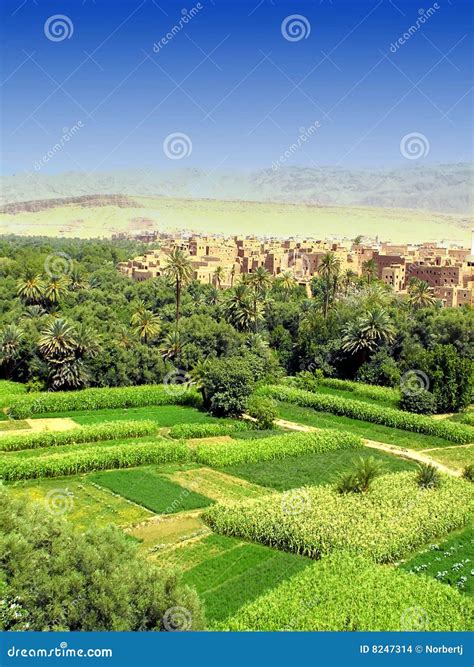

One of the most iconic and recognizable fertile areas in deserts is the oasis. Oases are pockets of lush greenery and freshwater sources surrounded by arid landscapes. They are often formed by underground water sources, such as springs or aquifers, that bring life-giving moisture to the surface.
Oases serve as vital refuges for both plant and animal life. They provide a much-needed source of water, nutrients, and shelter for desert organisms. The presence of water promotes the growth of vegetation, which, in turn, supports a diverse range of wildlife. Oases can be found in various forms, from small, secluded pools to expansive oases with extensive palm groves and abundant wildlife.
The fertility of oases is not limited to their water sources. The surrounding soil, enriched by organic matter and nutrients from decaying plant and animal matter, creates an ideal environment for plant growth. The combination of water, nutrients, and protection from the harsh desert conditions allows oases to become vibrant ecosystems, supporting a rich diversity of life.
The Role of Rainfall and Flash Floods
While oases provide a constant source of fertility, other areas in deserts experience sporadic bursts of fertility due to rainfall and flash floods. Deserts, though characterized by low precipitation, occasionally receive heavy rainfall, leading to temporary periods of abundance.
During these rare rainfall events, deserts transform into vibrant landscapes. The rain replenishes the soil with moisture, allowing dormant seeds to germinate and dormant plants to revive. This sudden burst of life attracts various wildlife, including birds, insects, and small mammals, creating a temporary ecosystem teeming with activity.
Additionally, flash floods, caused by heavy rainfall in nearby mountains, can bring water and sediment to otherwise dry riverbeds and canyons. These floods create fertile patches along the water's path, providing an opportunity for vegetation to thrive and support a unique set of organisms adapted to these temporary habitats.
Desert Adaptations for Fertility

The existence of fertile areas in deserts is made possible by the remarkable adaptations of desert organisms. Plants, in particular, have evolved various strategies to thrive in these harsh conditions.
- Drought Tolerance: Many desert plants have developed deep root systems that can tap into groundwater sources, ensuring access to water even during dry periods. Some plants also store water in their tissues, allowing them to survive prolonged droughts.
- Sun Protection: Desert plants often have waxy or hairy leaves that help reduce water loss through transpiration. Additionally, some plants have adapted to grow in a low, spreading pattern, minimizing their exposure to the intense desert sun.
- Seed Dormancy: Seeds of desert plants often have a built-in mechanism that prevents germination until favorable conditions arise. This strategy ensures that seeds remain dormant during dry periods, waiting for the arrival of rain to trigger their growth.
- Nectar Production: Certain desert plants produce an abundance of nectar to attract pollinators. By providing a valuable food source, these plants ensure their own reproduction and contribute to the overall fertility of the desert ecosystem.
Fertile Areas and Human Civilization

The presence of fertile areas in deserts has played a significant role in human civilization throughout history. Oases, in particular, have been crucial to the development of trade routes and the establishment of settlements in arid regions.
Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and the Nabataeans, recognized the importance of oases and utilized them as stopping points for trade caravans. These oases provided essential water sources, food, and rest for travelers, allowing them to traverse vast desert landscapes. The presence of fertile areas also led to the development of agriculture and the cultivation of crops, sustaining human populations in otherwise inhospitable environments.
Preserving Desert Fertility

The fertility of desert ecosystems is delicate and can be easily disrupted. Human activities, such as overgrazing, deforestation, and improper water management, can lead to the degradation of fertile areas. It is crucial to adopt sustainable practices and conserve these unique environments to ensure their long-term survival.
Conservation efforts often focus on protecting oases and their surrounding habitats. This includes implementing measures to prevent over-exploitation of water resources, promoting sustainable tourism, and raising awareness about the importance of desert ecosystems. By preserving these fertile areas, we can maintain the delicate balance between human needs and the preservation of biodiversity in deserts.
Conclusion

The existence of fertile areas in deserts is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of life. From the iconic oases to the temporary bursts of fertility during rainfall, these pockets of lush greenery thrive in the most challenging of environments. The unique adaptations of desert organisms, coupled with the presence of water and nutrients, create diverse and vibrant ecosystems that support a rich array of plant and animal life.
As we explore and appreciate the beauty of fertile areas in deserts, it is essential to recognize the fragility of these ecosystems and the importance of conservation. By understanding and protecting these unique habitats, we can ensure the continued existence of these remarkable oases and the biodiversity they support.
How do oases form in deserts?

+
Oases are formed by underground water sources, such as springs or aquifers, that bring water to the surface. These water sources provide a constant supply of moisture, allowing vegetation to thrive and creating a fertile oasis.
Can fertile areas in deserts support human settlements?

+
Yes, fertile areas like oases have played a crucial role in the development of human settlements in deserts. They provide essential water sources, food, and shelter, allowing communities to thrive in arid regions.
What adaptations do desert plants have to survive droughts?

+
Desert plants have developed deep root systems to access groundwater, store water in their tissues, and have waxy or hairy leaves to reduce water loss. Additionally, some plants have dormant seeds that wait for favorable conditions to germinate.
How can we protect fertile areas in deserts?

+
Protecting fertile areas in deserts involves sustainable water management, preventing overgrazing and deforestation, and promoting awareness about the importance of these ecosystems. Conservation efforts should focus on preserving oases and their surrounding habitats.