Introduction to the Generalized Method of Moments
The Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) is a powerful statistical technique used for estimating parameters in various models, particularly in econometrics and financial applications. It provides a flexible and robust approach to parameter estimation, making it a valuable tool for researchers and analysts. GMM allows for the estimation of models with potentially misspecified moments, making it a versatile and widely applicable method.
Understanding the GMM Concept
At its core, GMM is a moment-based estimation technique that utilizes sample moments to estimate model parameters. The method involves matching sample moments with their population counterparts, providing a way to estimate parameters based on the agreement between these moments. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with complex models or when traditional estimation methods, such as maximum likelihood estimation, may not be feasible or efficient.
Key Components of GMM
Moments and Moment Conditions
Moments play a crucial role in GMM. In statistics, moments represent the average value of a function of a random variable. GMM utilizes these moments, particularly the first and second moments (mean and variance), to construct moment conditions. Moment conditions are equations that equate the sample moments to their population counterparts, forming the basis for parameter estimation.
Weighting Matrix

A critical aspect of GMM is the weighting matrix, which assigns weights to the moment conditions. This matrix, often denoted as W, determines the relative importance of each moment condition in the estimation process. The choice of the weighting matrix can significantly impact the efficiency and robustness of the GMM estimator. Common choices include the identity matrix (equal weights) and the inverse of the sample covariance matrix.
Estimation Procedure
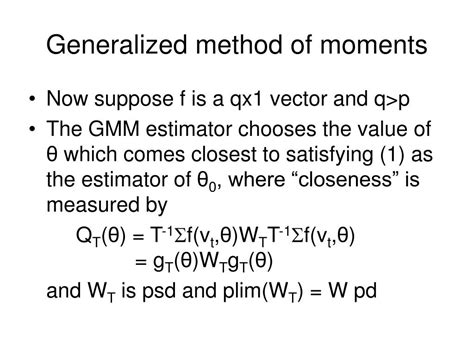
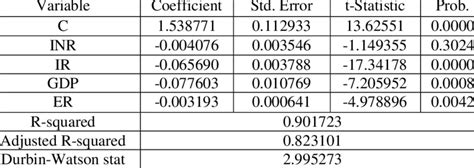
The GMM estimation procedure involves minimizing a quadratic form, known as the GMM objective function, subject to the moment conditions. This function measures the discrepancy between the sample and population moments, and the goal is to find the parameter values that minimize this discrepancy. The estimation process can be iterative, refining the parameter estimates until convergence is achieved.
Advantages of GMM

- Flexibility: GMM can handle a wide range of models, including those with nonlinearities and complex structures. It allows for the estimation of parameters in models with potentially misspecified moments, making it a versatile tool.
- Robustness: GMM is robust to misspecification, as it does not require the model to be correctly specified. It can still provide consistent estimates even if some of the moment conditions are not satisfied.
- Efficiency: With an appropriate weighting matrix, GMM estimators can achieve efficiency gains compared to other estimation methods. This makes GMM particularly useful when dealing with large datasets.
- Asymptotic Properties: GMM estimators possess desirable asymptotic properties, such as consistency and asymptotic normality. These properties ensure that the estimators converge to the true parameter values as the sample size increases.
Applications of GMM
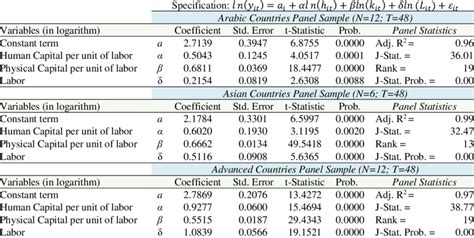
Econometrics

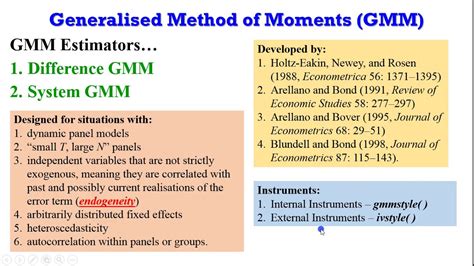
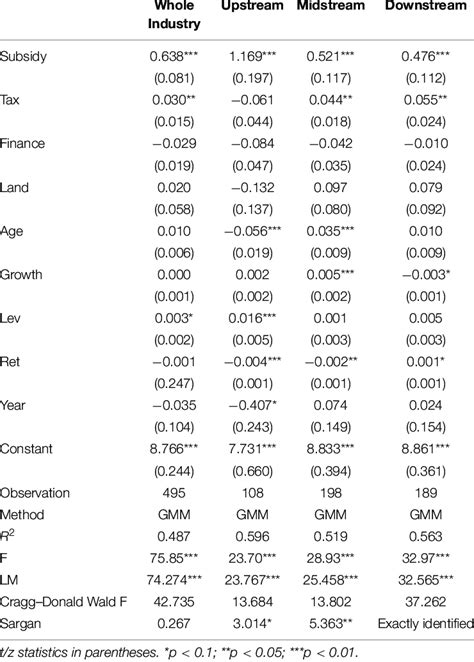
GMM is widely used in econometrics for estimating dynamic models, such as dynamic panel data models and time series models. It is particularly useful when dealing with endogeneity issues, where traditional methods may fail. GMM can also be applied to estimate models with unobserved heterogeneity or when dealing with panel data with fixed effects.
Financial Economics

In financial economics, GMM is employed to estimate asset pricing models, such as the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and the Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT). These models often involve moments related to asset returns, and GMM provides a robust framework for estimating their parameters. GMM is also used in estimating models for option pricing and portfolio optimization.
Other Fields

GMM finds applications beyond econometrics and finance. It is used in various fields, including engineering, biology, and social sciences, for parameter estimation in complex models. The method’s flexibility and robustness make it a valuable tool for researchers across disciplines.
Steps to Implement GMM

- Define the Model: Clearly specify the model to be estimated, including the parameters to be estimated and the moment conditions.
- Choose Moment Conditions: Select appropriate moment conditions that capture the relationship between the model and the data. These conditions should be based on economic theory or empirical evidence.
- Select a Weighting Matrix: Choose an appropriate weighting matrix, considering factors such as efficiency and robustness. Common choices include the identity matrix or the inverse of the sample covariance matrix.
- Estimate Parameters: Use an optimization algorithm to minimize the GMM objective function, subject to the moment conditions. This will provide estimates for the model parameters.
- Assess Estimation Quality: Evaluate the quality of the estimated parameters by examining the GMM objective function value and checking the moment conditions. If the moment conditions are not satisfied, the model may be misspecified, and further investigation is required.
Notes
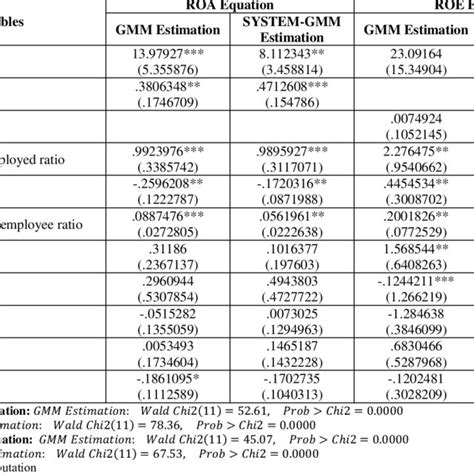
🌟 Note: GMM is a powerful tool, but it requires careful consideration of moment conditions and weighting matrices. Choosing the right moment conditions and weighting matrix is crucial for obtaining accurate and efficient estimates.
⚠️ Note: GMM estimators may not always be efficient, especially with small sample sizes or when the moment conditions are misspecified. In such cases, alternative estimation methods or model refinements may be necessary.
Conclusion

The Generalized Method of Moments is a versatile and robust statistical technique for parameter estimation. Its ability to handle complex models and misspecified moments makes it a valuable tool for researchers and analysts across various fields. By following the outlined steps and considering the provided notes, one can effectively implement GMM and obtain reliable estimates for their models.
FAQ

What is the main advantage of GMM over traditional estimation methods like maximum likelihood estimation (MLE)?

+
GMM is advantageous in its ability to handle misspecified models, making it more robust than MLE. While MLE requires the model to be correctly specified, GMM can still provide consistent estimates even with some misspecification.
Can GMM be used for non-linear models?

+
Yes, GMM is applicable to a wide range of models, including non-linear ones. It provides a flexible framework for estimating parameters in complex models, making it a valuable tool for various applications.
What are some common challenges in implementing GMM, and how can they be addressed?

+
One challenge is the choice of moment conditions and weighting matrices. It’s important to select appropriate moment conditions based on economic theory and choose a weighting matrix that balances efficiency and robustness. Additionally, GMM may not always be the most efficient estimator, especially with small samples or misspecified models. In such cases, alternative methods or model refinements may be considered.