Robotic manipulators are a fascinating and integral part of modern robotics, offering a wide range of applications and benefits. These mechanical arms, often resembling human arms in structure, are designed to perform various tasks with precision and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of robotic manipulators, exploring their types, working principles, advantages, and applications. Whether you're a robotics enthusiast, a student, or a professional in the field, this blog aims to provide an in-depth understanding of these remarkable machines.
Understanding Robotic Manipulators

Robotic manipulators, simply put, are automated arms capable of performing tasks that traditionally require human dexterity. They are designed to mimic the movement and functionality of human arms, allowing them to grasp, lift, and manipulate objects with precision. These manipulators find extensive use in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and research, revolutionizing the way tasks are executed.
Types of Robotic Manipulators

Robotic manipulators come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and environments. Here's an overview of the most common types:
Cartesian Robots

Also known as gantry robots, Cartesian robots move along three axes: X, Y, and Z. They are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, such as pick-and-place operations in manufacturing.
SCARA Robots

Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms (SCARA) are designed for assembly tasks. They offer a high degree of compliance in the X-Y plane, making them ideal for tasks like circuit board assembly.
Articulated Robots

Articulated robots have multiple, rotating joints, resembling a human arm's structure. They are highly flexible and can perform a wide range of tasks, making them suitable for various industries.
Cylindrical Robots

Cylindrical robots operate within a cylindrical workspace, with linear movements in the X and Z axes and rotational movement in the Y axis. They are commonly used for material handling and machine tending.
Spherical Robots
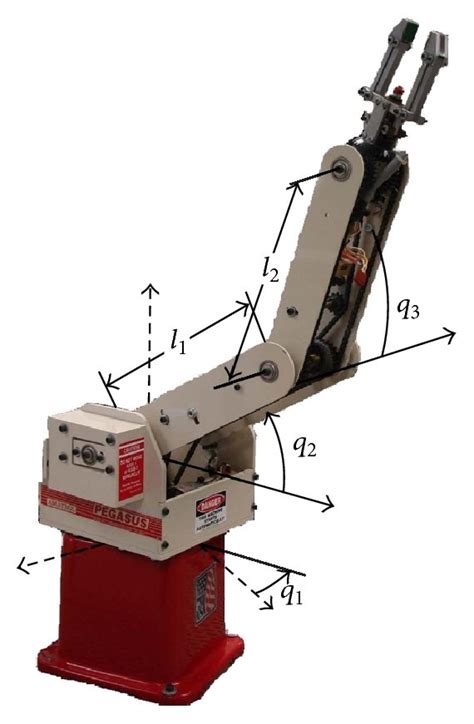
Spherical robots, also known as polar robots, have a spherical workspace with movements in the X, Y, and Z axes. They are often used for welding and material handling.
Working Principles of Robotic Manipulators

Robotic manipulators operate based on a combination of mechanical, electrical, and software components. Here's a simplified breakdown of their working principles:
Mechanical Structure

The mechanical structure of a robotic manipulator consists of joints and links. Joints provide rotational or linear movement, while links connect the joints and carry the payload.
Actuation
Actuators are responsible for generating the necessary force to move the manipulator's joints. Common actuators include electric motors, pneumatic or hydraulic systems, and even muscle wire.
Sensors

Sensors play a crucial role in providing feedback to the manipulator's control system. They include position sensors, force sensors, and vision systems, ensuring accurate and precise movements.
Control System

The control system is the brain of the robotic manipulator. It receives input from sensors, processes the data, and sends commands to the actuators to achieve the desired movements. Control systems can range from simple open-loop systems to complex closed-loop systems with advanced algorithms.
Advantages of Robotic Manipulators

Robotic manipulators offer numerous advantages over traditional manual labor or other automation systems. Here are some key benefits:
Precision and Accuracy

Robotic manipulators can perform tasks with a high degree of precision and accuracy, ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing and other processes.
Repeatability
They can repeat the same task over and over without fatigue or variation, maintaining consistency and reducing errors.
Versatility
With their modular design and advanced control systems, robotic manipulators can be easily reprogrammed for different tasks, making them highly versatile.
Safety
Robotic manipulators can work in hazardous environments, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries to human workers.
Efficiency and Speed
They can perform tasks at a much faster rate than humans, increasing productivity and reducing production times.
Applications of Robotic Manipulators

The versatility of robotic manipulators makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some key areas where they are commonly used:
Manufacturing
- Assembly of small components in electronics and automotive industries.
- Welding, painting, and material handling in heavy industries.
- Packaging and palletizing in food and beverage industries.
Healthcare
- Assisting in surgical procedures with precision and minimal invasion.
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy for patients.
- Handling and transporting hazardous materials in laboratories.
Research and Education
- Conducting experiments and simulations in research facilities.
- Teaching and training students in robotics and engineering programs.
Space Exploration
- Performing tasks in space stations and satellites.
- Exploring and collecting samples from other planets.
Choosing the Right Robotic Manipulator

Selecting the appropriate robotic manipulator for your specific application is crucial. Here are some factors to consider:
Workspace Requirements
Evaluate the workspace where the manipulator will operate. Consider the reach, payload capacity, and any specific environmental conditions.
Task Complexity
Analyze the complexity of the tasks to be performed. Different manipulators excel in different tasks, so choose one that aligns with your requirements.
Accuracy and Precision
If your application demands high accuracy and precision, opt for manipulators with advanced control systems and feedback mechanisms.
Integration and Compatibility
Ensure the manipulator can be easily integrated into your existing system and is compatible with other components.
Challenges and Future Developments

While robotic manipulators have come a long way, there are still challenges to overcome. Some of the key challenges include:
Flexibility and Adaptability
Developing manipulators that can easily adapt to changing environments and tasks remains a challenge.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Enhancing the collaboration between humans and robots to achieve seamless integration in various industries.
Advanced Control Systems
Improving control systems to handle complex tasks and provide real-time feedback for precise movements.
Safety and Ethics
Ensuring the safety of human workers and addressing ethical concerns related to the increasing use of robots in various sectors.
In Conclusion

Robotic manipulators have revolutionized the way tasks are executed across various industries. With their precision, versatility, and efficiency, they offer immense potential for improving productivity and safety. As technology advances, we can expect further developments in robotic manipulators, making them even more capable and integrated into our daily lives. Whether it's manufacturing, healthcare, or space exploration, robotic manipulators are undoubtedly a key component in shaping the future of automation.
What is the average lifespan of a robotic manipulator?
+The lifespan of a robotic manipulator can vary depending on factors such as usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions. On average, a well-maintained manipulator can operate for 10-15 years or more.
Can robotic manipulators work autonomously without human intervention?
+Yes, with advanced control systems and machine learning algorithms, robotic manipulators can operate autonomously. They can make decisions based on sensory input and perform tasks without direct human control.
How do robotic manipulators handle delicate or fragile objects?
+Robotic manipulators can be equipped with specialized end-effectors and force sensors to handle delicate objects with precision. By adjusting the force and speed of movements, they can ensure gentle and controlled interactions.
Are robotic manipulators suitable for small-scale businesses?
+Absolutely! Robotic manipulators are available in various sizes and configurations, making them suitable for businesses of all scales. They can be customized to fit specific workspace and task requirements, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
What are some common maintenance practices for robotic manipulators?
+Regular maintenance practices include lubricating joints, inspecting and replacing worn-out parts, calibrating sensors, and updating software. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and conducting periodic inspections can help ensure the longevity and optimal performance of robotic manipulators.