The 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten Meldal, and K. Barry Sharpless for their development of click chemistry and bioorthogonal chemistry, which has had a profound impact on the field of chemical biology and biomedical research. Among the various click reactions, the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation stands out as a powerful tool for labeling and imaging biomolecules in living systems. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation, exploring its principles, applications, and significance in modern chemical biology.
Understanding the Staudinger-Bertozzi Ligation

The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is a highly specific and bioorthogonal chemical reaction that enables the selective labeling and imaging of biomolecules in complex biological environments. It was first described by Carolyn Bertozzi and her colleagues in the early 2000s, building upon the seminal work of Nobel laureate Staudinger on the Staudinger reaction.
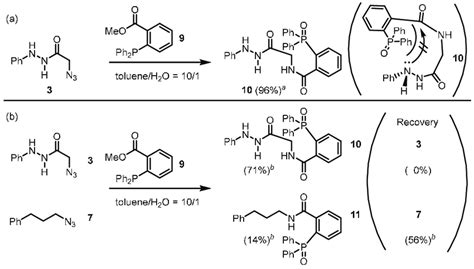
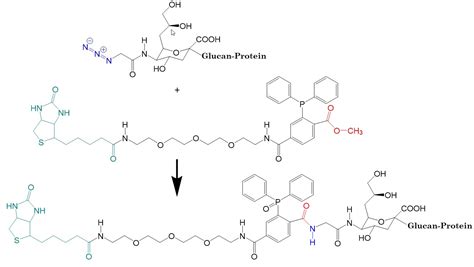
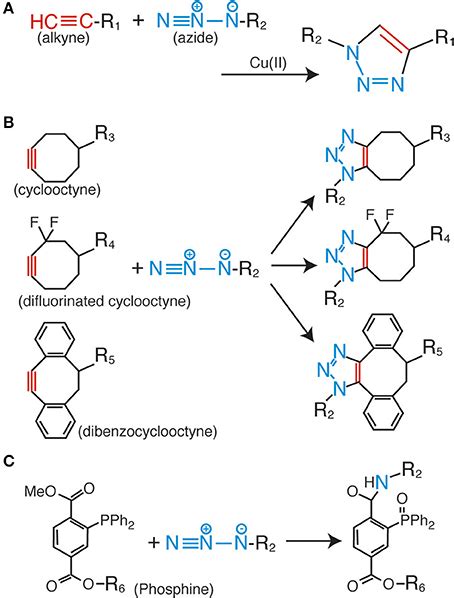
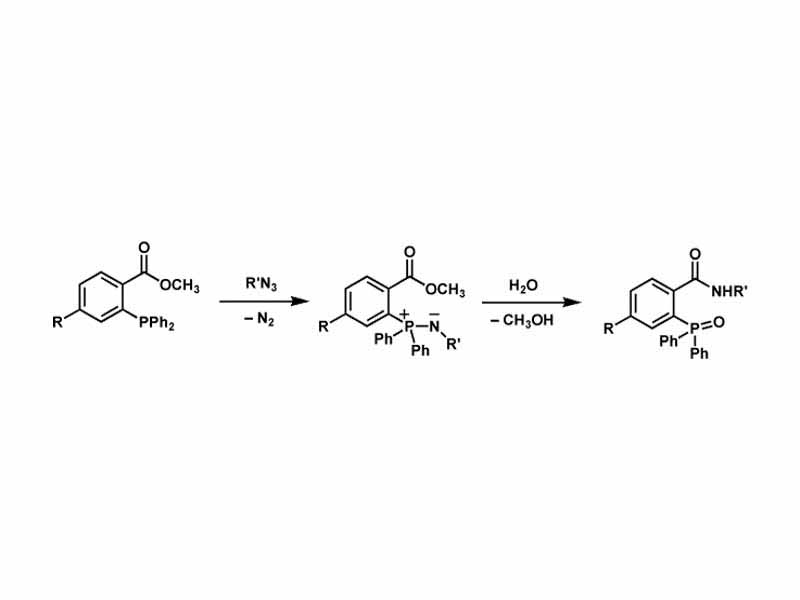
At its core, the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation involves a reaction between an azide group and a terminal alkyne in the presence of a catalyst, typically a phosphine or a metal catalyst. This reaction leads to the formation of a stable triazole linkage, which is highly resistant to biological degradation and can be used for a variety of applications.
Principles of the Staudinger-Bertozzi Ligation

The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is based on the following key principles:
- Bioorthogonality: The reaction is designed to occur only in the presence of specific functional groups, such as azides and alkynes, while being inert to other biological molecules and processes. This bioorthogonality ensures that the ligation reaction is highly selective and does not interfere with normal cellular functions.
- Catalysis: The reaction is typically catalyzed by a phosphine or a metal catalyst, which accelerates the formation of the triazole linkage. The choice of catalyst depends on the specific application and the desired reaction conditions.
- Regioselectivity: The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is highly regioselective, meaning it occurs at specific positions on the reactants. This selectivity allows for precise control over the labeling and imaging of biomolecules.
Applications of the Staudinger-Bertozzi Ligation

The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation has found numerous applications in chemical biology and biomedical research, including:
Biomolecule Labeling and Imaging
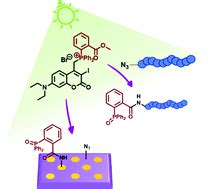
One of the most powerful applications of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is the labeling and imaging of biomolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. By incorporating azide or alkyne functional groups into these biomolecules, researchers can selectively label them with fluorescent or radioactive probes, enabling real-time imaging and tracking of their behavior in living systems.
Cell Surface Engineering
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation has been used to engineer the cell surface by modifying glycoproteins with specific functional groups. This allows for the study of cell-cell interactions, signal transduction, and the development of targeted therapies.
Drug Delivery and Targeting

The bioorthogonal nature of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation makes it an attractive tool for drug delivery and targeting. By conjugating drugs with azide or alkyne groups, researchers can selectively deliver them to specific cells or tissues, improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
Chemical Biology Research

The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation has revolutionized chemical biology research by providing a powerful tool for studying complex biological systems. It enables the investigation of protein-protein interactions, enzyme activity, and cellular signaling pathways, leading to a deeper understanding of biological processes.
Advantages of the Staudinger-Bertozzi Ligation
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation offers several advantages over traditional labeling and imaging techniques, including:
- Selectivity: The reaction is highly selective, allowing for precise labeling of specific biomolecules without interfering with other cellular components.
- Stability: The triazole linkage formed during the ligation is highly stable and resistant to biological degradation, ensuring long-lasting labeling and imaging.
- Versatility: The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation can be applied to a wide range of biomolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, making it a versatile tool for chemical biology research.
- In Vivo Imaging: The bioorthogonality of the reaction enables in vivo imaging of biomolecules, providing valuable insights into their behavior and dynamics in living organisms.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation has revolutionized chemical biology, there are still challenges to be addressed. Some of these challenges include:
- Catalyst Development: The development of new catalysts with improved reactivity, selectivity, and biocompatibility is crucial for expanding the applications of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation.
- Reaction Conditions: Optimizing reaction conditions, such as pH, temperature, and solvent choice, is essential for achieving efficient and specific ligation reactions.
- Biocompatibility: Ensuring the biocompatibility of the reagents and catalysts used in the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is vital for minimizing potential toxicity and off-target effects.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring new click reactions and bioorthogonal chemistries to further expand the toolkit for chemical biology. The integration of Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation with other cutting-edge technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9 and single-cell sequencing, holds great promise for advancing our understanding of complex biological systems.
Conclusion
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation has emerged as a powerful and versatile tool in chemical biology, enabling researchers to study complex biological systems with unprecedented precision and selectivity. Its applications in biomolecule labeling, cell surface engineering, drug delivery, and chemical biology research have revolutionized our understanding of biological processes. As the field continues to evolve, the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation and other bioorthogonal chemistries will undoubtedly play a crucial role in unlocking the mysteries of life.
FAQ

What is the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation?
+
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is a bioorthogonal chemical reaction that enables the selective labeling and imaging of biomolecules in complex biological environments. It involves the reaction between an azide group and a terminal alkyne, forming a stable triazole linkage.
What are the key advantages of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation?
+
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation offers advantages such as selectivity, stability, versatility, and the ability to perform in vivo imaging of biomolecules.
What are the main applications of the Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation in chemical biology?

+
The Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation is widely used for biomolecule labeling and imaging, cell surface engineering, drug delivery and targeting, and chemical biology research.
What are some future directions and challenges in the field of Staudinger-Bertozzi ligation and bioorthogonal chemistry?
+
Future directions include the development of new catalysts, optimization of reaction conditions, and ensuring biocompatibility. Challenges include expanding the range of applications and integrating with other cutting-edge technologies.