Introduction to Tick Testing

Tick testing is a crucial process that helps identify the presence of tick-borne diseases and provides valuable insights into potential health risks. With the increasing concern about tick-related illnesses, it’s essential to understand the steps involved in accurate tick testing. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the entire process, ensuring you have the knowledge to navigate tick testing with confidence.
Understanding Tick-Borne Diseases

Before delving into the testing process, let’s familiarize ourselves with tick-borne diseases. Ticks are tiny parasites that can transmit various pathogens to humans and animals, leading to a range of illnesses. Some common tick-borne diseases include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Ehrlichiosis, and Anaplasmosis. These diseases can have severe health consequences if left untreated, making early detection through testing vital.
Collecting Tick Samples

The first step in tick testing is collecting the tick sample. It’s important to handle ticks with care to avoid further contamination. Here’s a step-by-step guide to collecting tick samples:
- Identify the Tick: Carefully examine the tick to determine its species and stage of development. Different ticks carry different pathogens, so accurate identification is crucial.
- Remove the Tick: Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible. Pull upward with steady, even pressure to remove the entire tick. Avoid twisting or crushing the tick.
- Store the Tick: Place the tick in a clean, sealable container or a small plastic bag. Ensure the container is labeled with the date and location of the tick bite.
- Transportation: Keep the tick cool and dry during transportation to the testing facility. Avoid using alcohol or other chemicals that may damage the tick.
Choosing the Right Testing Facility

Selecting a reputable testing facility is crucial for accurate results. Look for facilities that specialize in tick testing and have experience handling various tick-borne diseases. Consider the following factors when choosing a testing facility:
- Accreditation: Opt for facilities accredited by recognized organizations, such as the College of American Pathologists (CAP) or the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA).
- Expertise: Choose a facility with a team of experienced scientists and technicians who have expertise in tick-borne disease testing.
- Testing Methods: Inquire about the testing methods used by the facility. Advanced molecular techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), offer higher sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional methods.
- Turnaround Time: Consider the facility’s turnaround time for test results. Prompt results can be crucial for timely treatment and management of tick-borne diseases.
Preparing the Tick Sample for Testing

Once you have collected and transported the tick sample, it’s time to prepare it for testing. Follow these steps to ensure proper sample preparation:
- Tick Identification: Confirm the tick’s species and stage of development with the help of a tick identification chart or a tick expert. This information is crucial for accurate testing.
- Sample Preservation: If the tick is still alive, you can preserve it by placing it in a small container with a moistened cotton ball. Ensure the container is securely sealed to prevent the tick from escaping.
- Sample Labeling: Clearly label the sample container with your contact information, the date of collection, and the location of the tick bite. This information is essential for accurate record-keeping and result interpretation.
Common Tick Testing Methods

Tick testing facilities employ various methods to detect tick-borne pathogens. Here are some commonly used testing methods:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a highly sensitive molecular technique that amplifies specific DNA sequences. It can detect the presence of tick-borne pathogens with great accuracy.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA is a widely used immunological test that detects antibodies produced by the body in response to tick-borne infections. It is useful for identifying past or current infections.
- Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA): IFA utilizes fluorescent dyes to detect specific antibodies in the blood. It is commonly used for the diagnosis of Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses.
- Western Blot: Western blot is a confirmatory test used to detect antibodies against specific tick-borne pathogens. It provides detailed information about the type and stage of infection.
Interpreting Tick Test Results

Interpreting tick test results requires expertise and careful consideration. Here’s a general overview of what you can expect:
- Positive Result: A positive result indicates the presence of tick-borne pathogens. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
- Negative Result: A negative result does not necessarily mean the absence of tick-borne diseases. False negatives can occur, especially if the tick is in the early stages of infection or if the test was performed too soon after the tick bite.
- Further Testing: In some cases, additional testing may be recommended to confirm or rule out the presence of tick-borne diseases. This can include blood tests, imaging studies, or further molecular testing.
Preventive Measures and Post-Test Care

Tick testing is just one aspect of managing tick-borne diseases. It’s important to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of tick bites and to follow post-test care instructions. Here are some key points to remember:
- Tick Bite Prevention: Wear protective clothing, use insect repellents, and regularly check for ticks when spending time outdoors.
- Prompt Tick Removal: If you find a tick attached to your skin, remove it promptly using fine-tipped tweezers. Proper tick removal can reduce the risk of disease transmission.
- Symptom Monitoring: After a tick bite, monitor yourself for any symptoms of tick-borne diseases, such as fever, rash, fatigue, or joint pain. Seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
- Follow-up Care: If your tick test results are positive, follow the recommended treatment plan provided by your healthcare provider. Complete the full course of antibiotics or other prescribed medications.
Tick Testing and Pet Safety

Ticks can also pose a threat to our furry friends. It’s essential to be aware of tick-borne diseases that affect pets and the steps to protect them. Here’s a brief overview:
- Tick Prevention for Pets: Use tick prevention products recommended by your veterinarian. Regularly inspect your pets for ticks, especially after outdoor activities.
- Tick Testing for Pets: If you find a tick on your pet, consider testing it for tick-borne diseases. Consult your veterinarian for guidance on tick testing and treatment options for your pet.
- Symptoms in Pets: Watch for signs of tick-borne diseases in your pets, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, joint pain, or changes in behavior. Prompt veterinary care is essential for their well-being.
Tick Testing Resources and Support

Navigating tick testing and tick-borne diseases can be overwhelming. Fortunately, there are resources and support available to guide you through the process. Here are some helpful links and organizations:
- Tick Testing Facilities - The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides a list of tick testing facilities across the United States.
- Tick-Borne Disease Alliance - The Tick-Borne Disease Alliance offers educational resources, advocacy, and support for individuals affected by tick-borne diseases.
- Lyme Disease Association - The Lyme Disease Association provides information, support, and research funding for Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses.
- Local Health Departments - Contact your local health department for guidance and resources specific to your region.
Conclusion
Tick testing is a critical step in the diagnosis and management of tick-borne diseases. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, you can ensure accurate results and take the necessary steps to protect your health and the health of your loved ones. Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to successfully managing tick-borne illnesses. Stay informed, take preventive measures, and seek professional guidance when needed. Together, we can navigate the world of tick testing with confidence and ensure a healthier future.
🌿 Note: Always consult with healthcare professionals or veterinarians for personalized advice and treatment plans regarding tick-borne diseases.
FAQ
How long does it take to get tick test results?

+
The turnaround time for tick test results can vary depending on the testing facility and the specific test performed. Generally, results can be expected within a few days to a couple of weeks. It’s best to inquire about the estimated turnaround time when submitting your tick sample.
Can tick tests be performed on humans directly, without removing the tick?
+
No, tick tests are typically performed on the tick itself rather than directly on humans. Removing the tick and submitting it for testing provides a more accurate assessment of potential tick-borne infections.
Are there any home testing kits available for tick-borne diseases?

+
While there are home testing kits available for certain tick-borne diseases, it’s important to note that they may not provide the same level of accuracy and reliability as tests performed by accredited laboratories. Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the most appropriate testing method.
Can tick-borne diseases be cured, or do they require lifelong management?

+
The treatment and management of tick-borne diseases depend on the specific disease and its severity. Some tick-borne diseases can be effectively treated with antibiotics or other medications, while others may require long-term management and monitoring. It’s crucial to follow the advice of healthcare professionals for the best course of action.
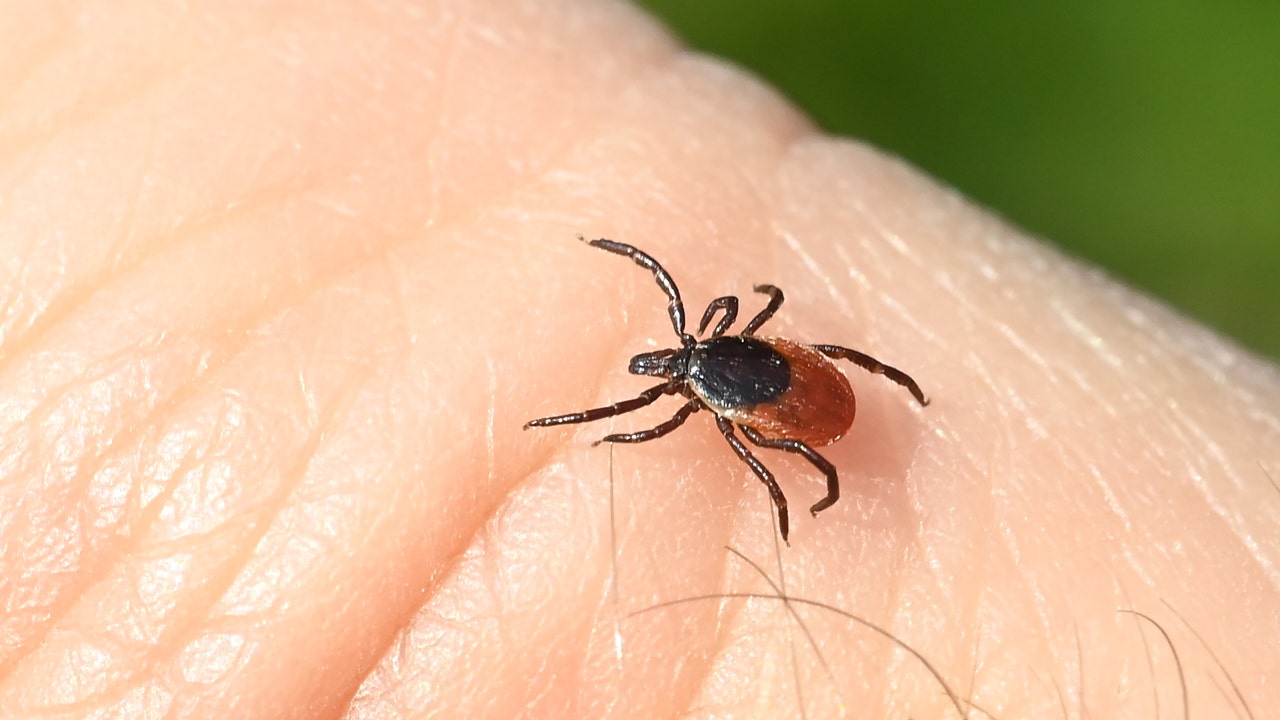
What are the early signs and symptoms of tick-borne diseases?

+
Early signs and symptoms of tick-borne diseases can vary but may include fever, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, and a distinctive rash (in the case of Lyme disease). It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms after a tick bite.