Fructose, a simple sugar found naturally in fruits, has been a topic of interest and controversy in recent years. With its sweet taste and potential health implications, it's time to delve into the ultimate truth about fructose and separate fact from fiction.
The Sweet Side of Fructose
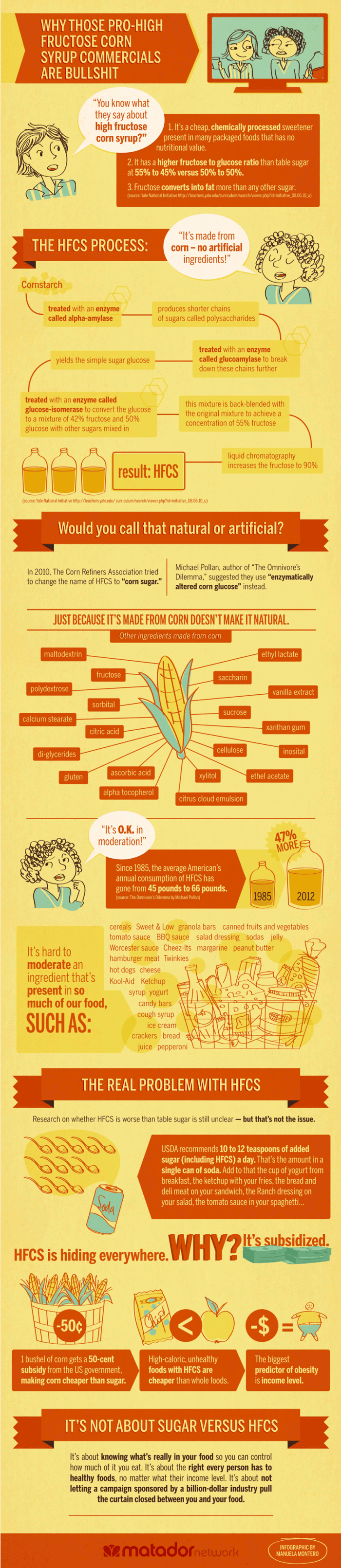
Fructose, often referred to as fruit sugar, is a carbohydrate that provides a natural sweetness to various foods. It is an essential component of many fruits and vegetables, contributing to their delicious taste and nutritional value.
Here are some key points to understand about fructose:
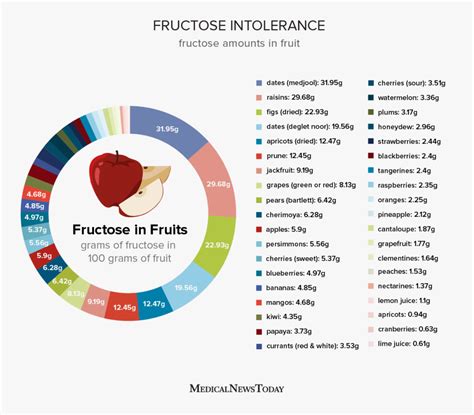
- Natural Occurrence: Fructose is present in numerous fruits, such as apples, oranges, and berries. It is also found in some vegetables like onions and artichokes.
- Sweetness: Fructose is known for its high sweetness intensity, often used as a natural sweetener in various food products.
- Caloric Content: Like other sugars, fructose provides calories. It has the same caloric value as glucose, with approximately 4 calories per gram.
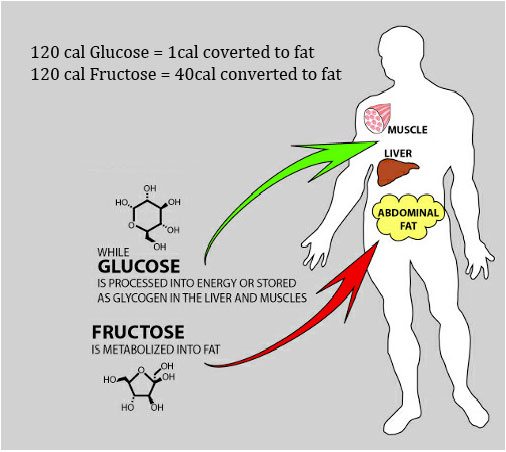
- Metabolism: Fructose is metabolized differently than glucose. It is primarily processed by the liver, which can lead to potential health concerns when consumed in excess.
The Impact of Fructose on Health

While fructose is a natural component of many healthy foods, its excessive consumption has raised concerns about its impact on health. Let's explore some of the key issues:
1. Weight Gain and Obesity

Excessive fructose intake has been linked to weight gain and obesity. When consumed in large amounts, especially in the form of added sugars, fructose can contribute to an excess of calories, leading to an energy imbalance and potential weight gain.
2. Metabolic Syndrome

High fructose consumption has been associated with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess body fat around the waist. Metabolic syndrome can increase the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
3. Liver Health

As mentioned earlier, fructose is primarily metabolized by the liver. Excessive fructose intake can put a strain on the liver, potentially leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This condition is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, which can impair liver function.
4. Blood Sugar Control
Fructose has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to glucose. However, when consumed in large amounts, especially in the form of added sugars, it can contribute to insulin resistance and impaired blood sugar control over time.
Fructose vs. Added Sugars
It's important to distinguish between naturally occurring fructose in whole fruits and added sugars containing fructose. Whole fruits provide not only fructose but also fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious choice.
On the other hand, added sugars, such as high-fructose corn syrup and table sugar, are often used in processed foods and beverages. These added sugars can provide excess calories and contribute to health issues when consumed in excess.
Moderation is Key

The key to maintaining a healthy relationship with fructose lies in moderation. Here are some tips to consider:
- Choose Whole Fruits: Opt for whole, fresh fruits instead of processed fruit juices or products with added sugars. Whole fruits provide essential nutrients and fiber, making them a healthier choice.
- Limit Added Sugars: Be mindful of the added sugars in your diet. Read food labels and choose products with minimal added sugars.
- Practice Portion Control: Even natural sugars like fructose should be consumed in moderation. Be aware of your portion sizes and avoid excessive intake.
- Balance Your Diet: Ensure your diet is well-balanced, including a variety of whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
The Role of Fructose in a Healthy Diet
Fructose can be a part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced approach. Here's how it can benefit your overall health:
- Natural Sweetness: Fructose provides a natural sweetness to foods, reducing the need for artificial sweeteners or excessive added sugars.
- Nutritional Value: Whole fruits containing fructose are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, contributing to a nutritious diet.
- Digestive Health: The fiber found in whole fruits can promote a healthy digestive system and prevent constipation.
Fructose and Athletes

Fructose can be particularly beneficial for athletes due to its unique metabolic properties. Here's how it can support athletic performance:
- Energy Source: Fructose can be an efficient energy source for athletes, especially during prolonged exercise. It can be metabolized by the liver to produce glucose, providing a steady supply of energy.
- Glycogen Repletion: Fructose can help replenish glycogen stores in the liver, which are crucial for sustained energy during intense workouts or competitions.
- Muscle Recovery: Consuming fructose after exercise can aid in muscle recovery by promoting glycogen synthesis and reducing muscle soreness.
Fructose in Special Diets

Fructose may require special consideration for individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions. Here are some points to consider:
1. Fructose Malabsorption

Some individuals may have difficulty absorbing fructose, leading to gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. These individuals should limit their fructose intake and opt for low-fructose foods.
2. Diabetes

Individuals with diabetes should monitor their fructose intake, as it can still impact blood sugar levels. However, when consumed as part of a balanced diet and in appropriate amounts, fructose can be a suitable option.
3. Low-FODMAP Diet
Fructose is one of the FODMAPs (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols), which are short-chain carbohydrates that can trigger digestive symptoms in some individuals. Those following a low-FODMAP diet should limit their fructose intake.
FAQs
Is fructose bad for you?

+
Fructose itself is not inherently bad. When consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, it can be a natural and healthy source of sweetness. However, excessive intake, especially in the form of added sugars, can lead to various health issues.
Can fructose cause weight gain?
+
Excessive fructose intake, particularly in the form of added sugars, can contribute to weight gain. It provides calories, and when consumed in excess, it can lead to an energy imbalance, resulting in weight gain over time.
Is fructose better than glucose for blood sugar control?

+
Fructose has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to glucose. However, it's important to note that excessive fructose intake can still contribute to insulin resistance and impaired blood sugar control over time.
Can fructose be beneficial for athletes?
+Yes, fructose can be particularly beneficial for athletes due to its unique metabolic properties. It can provide a steady energy source, aid in glycogen repletion, and support muscle recovery after intense exercise.
How can I reduce my fructose intake?
+To reduce your fructose intake, focus on limiting added sugars in your diet. Choose whole, fresh fruits instead of processed fruit juices or products with added sugars. Read food labels and opt for low-fructose alternatives when necessary.
Conclusion

Fructose, when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet, can be a natural and healthy source of sweetness. It provides essential nutrients and supports overall health. However, excessive intake, especially in the form of added sugars, can lead to various health concerns. By being mindful of your fructose consumption and choosing whole, natural foods, you can enjoy the benefits of fructose while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.