Rational Choice Voting, often referred to as RCV, is a voting system designed to address the limitations of traditional voting methods. It aims to provide a more accurate representation of voters' preferences and facilitate the election of candidates who truly reflect the will of the majority. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Rational Choice Voting, exploring its mechanics, benefits, and potential impact on democratic processes.
Understanding Rational Choice Voting

Rational Choice Voting is an innovative electoral system that employs a ranked-choice approach. Unlike the simple majority or plurality voting systems, RCV allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference. This ranking system ensures that voters can express their true preferences without the fear of wasting their vote or contributing to the election of a less-preferred candidate.
How Does Rational Choice Voting Work?

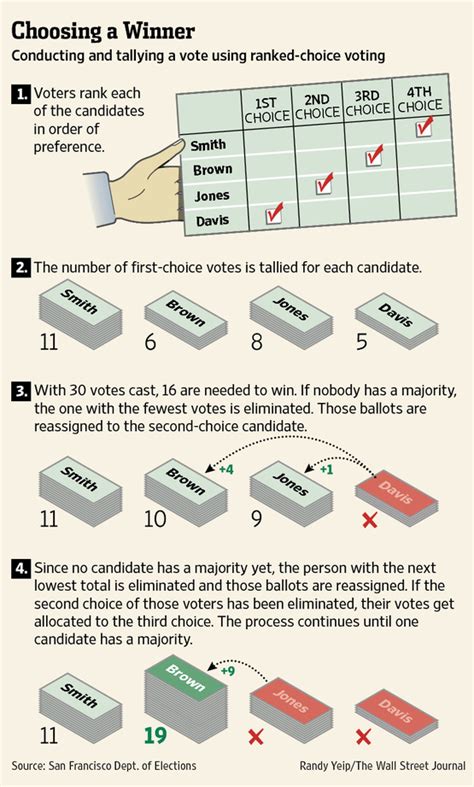
The process of Rational Choice Voting can be broken down into several steps:
- Casting a Vote: Voters are provided with a ballot that lists all the candidates running for a particular position. Alongside each candidate's name, there is a space for voters to indicate their preference. Voters can rank as many or as few candidates as they wish.
- Counting the First Preferences: Once the votes are cast, the counting process begins. The first step is to count the first preferences, which are the voters' top choices. The candidate with the most first-preference votes is identified.
- Eliminating Least-Preferred Candidates: If the candidate with the most first-preference votes has secured more than 50% of the votes, they are declared the winner. However, if no candidate reaches this threshold, the candidate with the fewest first-preference votes is eliminated.
- Reallocating Votes: The votes cast for the eliminated candidate are then reallocated to the next-ranked candidate on each ballot. This process continues until a candidate reaches the majority threshold or only one candidate remains.
- Declaring the Winner: Once a candidate secures more than 50% of the votes, they are declared the winner of the election.
Benefits of Rational Choice Voting

Rational Choice Voting offers several advantages over traditional voting systems:
- Enhanced Voter Satisfaction: With RCV, voters can rank candidates based on their true preferences, eliminating the need to strategically vote for a less-preferred candidate to avoid a worse outcome.
- Reduced Vote Splitting: In traditional voting systems, similar candidates can split the vote, leading to the election of a candidate with less support. RCV minimizes this issue by allowing voters to rank candidates, ensuring the election of the candidate with the broadest support.
- Encouraging Candidate Diversity: RCV encourages a wider range of candidates to run for office, as voters can rank multiple candidates without fear of wasting their vote. This fosters a more diverse and representative political landscape.
- Efficient Use of Resources: The ranked-choice system streamlines the election process, reducing the need for multiple rounds of voting or costly runoff elections.
Implementing Rational Choice Voting

Implementing Rational Choice Voting requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some key steps to ensure a successful transition:
- Educating Voters: It is crucial to educate voters about the new voting system to ensure they understand how to rank candidates effectively. Providing clear and concise information about the process can help alleviate any confusion or skepticism.
- Training Election Officials: Election officials and staff must be trained to administer and count votes accurately. This includes understanding the ranked-choice system and the specific procedures for vote tabulation.
- Updating Voting Infrastructure: The voting infrastructure, including ballot design and counting systems, may need to be updated to accommodate the ranked-choice system. This ensures a smooth and efficient voting process.
- Pilot Testing: Before full implementation, it is beneficial to conduct pilot tests or trial runs to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement. This allows for adjustments to be made before the official election.
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
Despite its numerous benefits, Rational Choice Voting has faced some skepticism and concerns. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for the successful adoption of the system:
- Complexity: Some argue that RCV is too complex for voters to understand. However, with proper education and clear instructions, voters can easily grasp the concept of ranking candidates.
- Vote Splitting: Critics claim that RCV can still lead to vote splitting, especially if voters do not rank candidates strategically. However, the reallocation of votes during the counting process mitigates this issue, ensuring that the candidate with the broadest support wins.
- Manipulation: There is a concern that RCV can be manipulated by strategic voting. While this is a possibility, it is important to note that strategic voting exists in all voting systems. RCV, however, provides voters with more options and a greater say in the outcome.
🌟 Note: It's crucial to emphasize that Rational Choice Voting aims to improve the democratic process by empowering voters and ensuring a more accurate representation of their preferences.
Real-World Examples

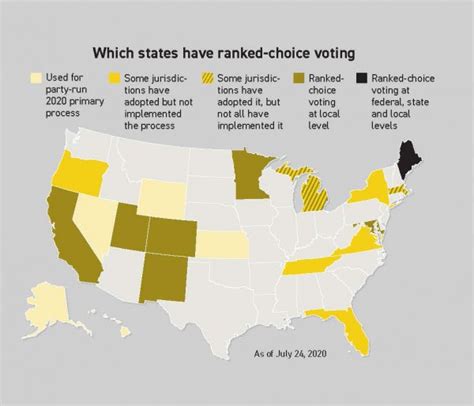
Rational Choice Voting has been implemented in various jurisdictions around the world, with notable success. Here are a few examples:
- San Francisco, USA: San Francisco has been using RCV since 2004 for municipal elections. The system has been well-received and has led to increased voter participation and satisfaction.
- Ireland: Ireland has utilized RCV, known as the Single Transferable Vote (STV), for its parliamentary elections since 1922. The system has contributed to a more proportional representation of political parties.
- Australia: Australia employs RCV for its federal elections, as well as for various state and local elections. The system has been in place for over a century and has proven to be an effective method of electing representatives.
The Impact of Rational Choice Voting
The adoption of Rational Choice Voting can have a significant impact on democratic processes and political landscapes:
- Increased Voter Turnout: By allowing voters to rank candidates, RCV encourages greater participation in the electoral process. Voters feel more engaged and empowered, leading to higher turnout rates.
- Improved Candidate Selection: RCV promotes the election of candidates who truly represent the will of the majority. It reduces the influence of strategic voting and ensures that the candidate with the broadest support wins.
- Promoting Political Diversity: The ranked-choice system encourages a wider range of candidates to run for office, fostering a more diverse and inclusive political environment. This can lead to better representation and policy-making.
FAQs

How does Rational Choice Voting differ from traditional voting systems?

+
Rational Choice Voting differs from traditional voting systems by allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference. This ranked-choice system ensures that voters can express their true preferences and reduces the impact of vote splitting.
Is Rational Choice Voting more complex for voters to understand?

+
While RCV may seem complex at first, proper education and clear instructions can help voters understand the ranking process. With practice, voters can easily rank candidates based on their preferences.
Can Rational Choice Voting be manipulated by strategic voting?

+
Strategic voting exists in all voting systems, including RCV. However, RCV provides voters with more options and a greater say in the outcome, making it less susceptible to manipulation compared to traditional systems.
Conclusion

Rational Choice Voting offers a promising alternative to traditional voting systems, empowering voters and ensuring a more accurate representation of their preferences. By implementing RCV, democratic processes can become more inclusive, diverse, and reflective of the will of the people. As we continue to explore and refine our electoral systems, Rational Choice Voting stands as a compelling option for achieving fair and representative elections.